There is a risk of being infected by worms without leaving your home. Various helminth patterns can be found on household items, banknotes, dishes, food and drinking water.
Parasites enter the human body in a way that is convenient for them: they can enter the digestive system through food, water, dirty hands, or insect bites.
Furthermore, helminths affect certain internal organs, use the resources of the human body, cause mechanical damage and actively reproduce. Their vital processes are accompanied by unpleasant and often dangerous symptoms and damage to various organs.
How to recognize intestinal worms
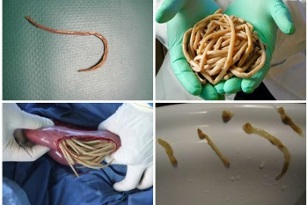
Intestinal worms unite a group of diseases caused by different types of worms. The most common are ascariasis (roundworms), enterobiasis (pinworms), ankylostomatidosis (hookworms). These parasites live in the lumen of the human gut, feed on its contents, and may be suspected of having a number of characteristic symptoms:
- Dramatic weight loss without changing diet and physical activity. Intestinal helminths use the nutrients of the human body as a source of energy for growth and reproduction, and with their means used to fix them in the intestine (suckers, hooks) damage their walls and interfere with the absorption of the remaining trace elements.
- Stomach and navel pain, rectal itching are caused by the movement of worms, the mechanical damage they cause, and the release of larvae or adults from the body into the external environment.
- Various gastrointestinal disorders: diarrhea or constipation, bloating, mucus, presence of foam or blood in the stool, nausea, vomiting. In some cases, adult parasites are found in the stool.
- The human body can react to the appearance of parasites with an allergic reaction, poisoning phenomena caused by the waste products of helminths. More often it occurs in itching of the skin, redness of certain areas, rashes (blisters, blisters of different sizes).
Diagnosis of intestinal helminthiasis includes stool examination, clinical and biochemical blood tests (eosinophilia, leukocytosis) and, if necessary, body ultrasound data.
Signs of parasites appearing in the liver
The human liver accumulates large amounts of nutrients and has intense blood circulation, which is convenient for parasites. Common hepatic helminthiasis: fascioliasis, opisthorchiasis, dicroceliosis caused by worms in the group of liver deposits.
You can define them by specific characteristics:

- Acute pain in the right hypochondrium is caused by the mechanical action of helminths. Thus, echinococcus forms cysts in organ tissues, provoking the development of inflammatory processes or even necrosis.
- Adult worms (roundworms) can block the bile ducts, causing the bile to flow out, the digestive process in the body is difficult, and the patient shows signs of jaundice. A person’s visible mucosa gets a yellow tint, and as the pathology develops, the skin also becomes stained.
- Non-specific symptoms of the appearance of parasites will be deterioration of the general condition of the body, weight loss, nausea, depression.
Blood is given for analysis to clarify the diagnosis. Leukocytosis, eosinophilia are detected, and biochemical tests indicate an increase in the activity of liver enzymes (ALT, AST). Ultrasound will show damage to the liver in the body: enlargement, inflammation and in some cases parasitic cysts.
What indicates the presence of lungworms
Some parasites (globular worm, toxoplasma, echinococcus, tsenur) can enter the lungs of a person with blood or lymph flow from the gastrointestinal tract. They multiply in the alveoli, making it difficult to breathe, and some species (echinococcus unicameral) form cysts, damaging the structure of the organ.
It can be difficult to determine the presence of parasites in the lungs because the symptoms are similar to those of viral and non-infectious respiratory diseases (bronchitis, ARVI). Cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, fever indicate the need for further examination of the patient's body.
The X-ray method will be the most informative for diagnosing pulmonary helminthiasis. The images show the lesions in the human body caused by echinococcus (cysts) and bovine tapeworms (fibrous formations), which must then be distinguished from tumor, cysts of various etiologies, and pneumonia.
Blood-borne parasites
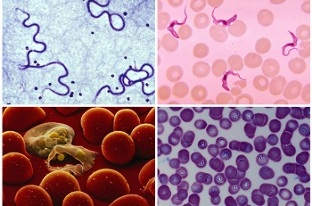
Protozoa unicellular worms are found in the lumen of blood vessels. Babesia, plasmodia (malaria plasmodium), trypanosome, microfilariae, schistosoma cause dangerous diseases that pose a threat to human life.
Destroying shaped elements disrupts the body's energy metabolism and blocks the supply of nutrients to organs and tissues.
Diagnosis ofIn most cases, human infection occurs after the bites of insects or ticks. After a while, signs of anemia develop in the body: pallor, followed by mucosal cyanosis, dizziness, sudden weight loss, and deterioration in health. Without timely medical care, blood parasites can pose a serious threat to human life.
involves microscopic examination of the blood to find single-celled parasites and destroyed red blood cells and to determine the type of worm. Treatment is long-term, performed on site under the supervision of a qualified physician.
Unusual parasitic habitats
Certain types of helminths can penetrate the human heart, subcutaneous tissues (dirofilariae), brain, and spinal cord (cysticercus, echinococcus). It can become infected not only in exotic countries, but also if you consume familiar, improperly heat-treated foods and pets can become carriers. Signs of invasion depend on the degree of damage to a particular organ.
Worms in the brain can form cysts, fibrous formations that cause nerve phenomena.
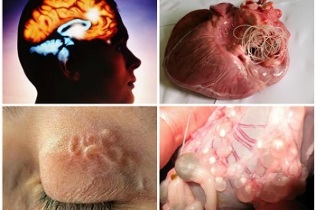
Headache of unexplained etiology, limb tremor (tremor), change in tactile sensitivity, impaired coordination of movements, sharp deterioration of hearing and vision - signs of invasion from worms and their larvae.
Adult parasites are visually visible under the skin, usually with itching and tingling, and in the eyes, ear canals, and other places.
What to do if you see signs of a worm infection
Diseases of parasitic etiology are treated under medical supervision after all necessary examinations and determination of the type of parasites. Prescribe narrow or broad spectrum anthelmintics, perform restorative and symptomatic therapy, help remove worms from the body. In some cases, surgery is recommended.
The prognosis for most diseases is favorable if treatment is started on time. If you postpone a visit to the doctor or take medication on your own, the healing process can be delayed and many types of parasites can damage vital organs or the body system or even lead to death.



























